When you stop and think about it, the human body is an absolute marvel. It’s like a living, breathing machine that somehow keeps running smoothly without us even having to think about it (most of the time). From the beating of your heart to the way you process information, your body is a masterpiece of design and functionality.
So, let’s take a little trip through the human body and explore some of the incredible systems that keep us alive and kicking. Trust me, after reading this, you’ll appreciate your body even more (and maybe give it a little extra care, too).
🧠 The Brain: The Control Center
Let’s start with the brain, the boss of the entire operation. Weighing about three pounds, this soft, wrinkled organ is responsible for pretty much everything you do. From deciding to grab a cup of coffee to solving complex math problems (if you’re into that), the brain is the ultimate multitasker.
The brain sends signals through the nervous system, which is made up of nerves that stretch from head to toe. It’s like the internet of your body, transmitting messages at lightning speed to keep you moving, thinking, and even feeling emotions. You can think of it as your body’s very own supercomputer.
But here’s the kicker: despite all of its complexity, the brain is still not fully understood. We know it controls thoughts, memories, and motor skills, but there’s so much more to explore. For example, have you ever wondered how the brain can remember the smell of fresh-baked cookies from your childhood? It’s this incredible organ that makes it all happen.
💪 Muscles and Movement: The Power to Move
Now, let’s move on to the muscles, which give your body the ability to move. There are over 600 muscles in the human body, and they come in all shapes and sizes. From the big muscles in your legs (hello, quads and calves!) to the tiny ones that control the movement of your eyes, muscles are essential for every single movement you make.
Muscles are divided into three types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscles are the ones you’re probably most familiar with — they’re the ones you can flex and see when you exercise. These muscles help you perform everyday tasks, like lifting groceries or running to catch the bus.
Smooth muscles, on the other hand, are found in places like your stomach and blood vessels. They’re not under your conscious control, but they’re working hard to help digest food and keep your blood flowing.
Then, there’s cardiac muscle, which makes up the heart. It’s a specialized muscle that never gets tired and keeps pumping blood throughout your life — now that’s dedication.
❤️ The Heart: The Lifeline
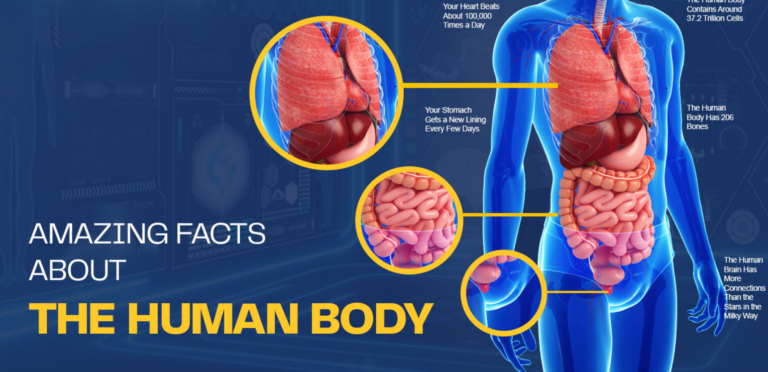
Let’s talk about your heart, the ultimate workhorse of the human body. This little muscle (about the size of your fist) pumps blood throughout your body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to every cell. It beats about 100,000 times a day, sending 2,000 gallons of blood through your arteries.
The heart has four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. The right side of the heart pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen, and the left side pumps oxygenated blood to the rest of the body. It’s like a high-performance engine that keeps running 24/7, without needing any maintenance (as long as you take care of it, of course).
But here’s something you might not know: while the heart may seem like an automatic machine, it’s influenced by everything around you. Stress, exercise, and even your emotions can affect your heart rate. So, keeping your heart happy by staying active and managing stress is important for long-term health.
💧 The Digestive System: Fueling the Body
Eating is something we all do multiple times a day, but have you ever wondered what happens after that delicious meal hits your stomach? Enter the digestive system, which works tirelessly to break down food and absorb nutrients.
When you eat, food travels through your mouth, down your esophagus, and into your stomach. Here’s where the fun begins. Your stomach is like a blender, mixing food with digestive juices to turn it into a liquid substance called chyme. This chyme then enters the small intestine, where the majority of digestion and nutrient absorption takes place.
The small intestine is lined with tiny hair-like structures called villi that grab nutrients and send them into your bloodstream. After the nutrients are absorbed, the leftover material moves into the large intestine, where water is absorbed and the rest is turned into waste that leaves the body.
And did you know your gut microbiome plays a huge role in digestion? There are trillions of bacteria living in your intestines that help break down food and produce certain vitamins. It’s like having a whole team of microscopic helpers working for you.
🫁 The Respiratory System: Breathing Life
Every time you take a breath, you’re using your respiratory system, which ensures that oxygen gets into your body and carbon dioxide is expelled. The process starts when you inhale air through your nose or mouth, and it travels down the windpipe (trachea) into your lungs. Inside the lungs, oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide in tiny air sacs called alveoli.
Your diaphragm, a large muscle beneath the lungs, helps you breathe by contracting and relaxing, which makes air flow in and out of your lungs. Without your respiratory system, your body wouldn’t get the oxygen it needs to fuel all its functions. And considering the fact that we breathe about 20,000 times a day, it’s pretty impressive that this system works almost automatically without us even thinking about it.
🦴 The Skeleton: The Body’s Framework
Let’s not forget about your skeleton, which serves as the body’s framework. Made up of 206 bones, the skeleton not only provides structure but also protects vital organs like the brain, heart, and lungs. Without bones, we’d be a floppy mess, literally just a pile of muscles and skin.
Bones are also where blood cells are made. Inside certain bones, like your femur, is bone marrow, where red and white blood cells are produced. And your bones aren’t just static structures — they’re constantly remodeling. In fact, your bones are replaced every 10 years or so.
Your skeleton works closely with the muscles to enable movement. Joints like your knees and elbows act as hinges, and your spine (made up of vertebrae) allows you to bend and twist. Without your skeleton, you wouldn’t be able to stand, walk, or even sit up straight.
🚨 The Immune System: The Body’s Defense
Now, let’s talk about your immune system, the unsung hero that keeps you safe from harmful invaders. Every day, your body is exposed to bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens that could make you sick. Thankfully, your immune system is there to defend you.
Your body has several lines of defense, including the skin, which acts as a physical barrier, and the white blood cells, which hunt down and destroy harmful invaders. When you get a cold, for example, your immune system kicks into gear by sending white blood cells to fight the virus. And when you get a vaccine, your immune system learns how to recognize and fight off specific threats in the future.
🧘♀️ The Human Body: A Balanced System
It’s pretty clear by now that the human body is an intricate, interconnected system that relies on every part to function properly. It’s like a perfectly designed machine where each part has a specific job, and everything works in harmony to keep you alive and thriving. So, take care of it! Exercise, eat well, get enough sleep, and always listen to your body’s signals.
Whether you’re running a marathon or simply enjoying a cup of coffee, your body is the amazing vessel that makes it all possible. And the best part? There’s always more to learn about this incredible system, making it a lifelong adventure to discover just how truly remarkable we are.





































































































0 Comments