Here are detailed facts about Shah Jahan, the Mughal emperor best known for commissioning the Taj Mahal:
When you think of the Mughal Empire, the first image that likely pops into your mind is the Taj Mahal—that majestic white marble structure, glowing in moonlight, standing as a symbol of love and loss. And behind this monument is the man who made it all happen: Shah Jahan, the fifth emperor of the Mughals.
But Shah Jahan was much more than just the guy who built the Taj. His story is a mix of royal grandeur, deep romance, brutal power struggles, and a surprisingly poetic soul. Let’s take a chill journey through his fascinating life.
Born to Rule, Raised in Royalty
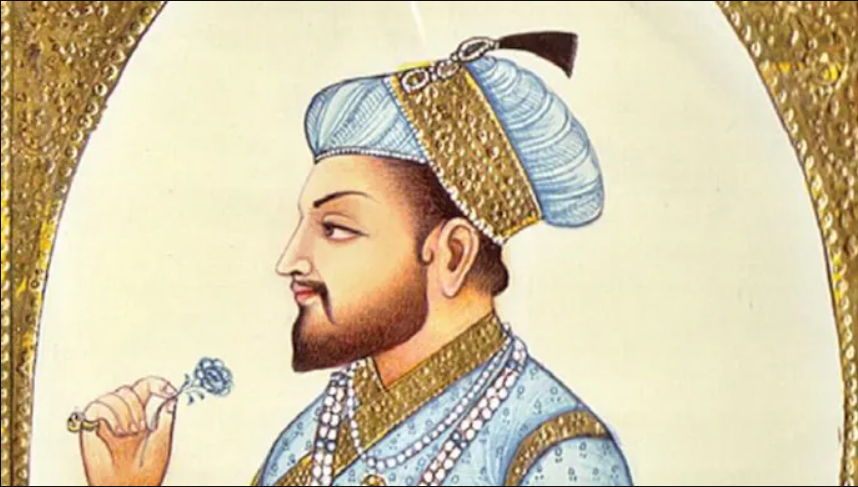

Shah Jahan was born as Prince Khurram on January 5, 1592, in Lahore (modern-day Pakistan), during the reign of his grandfather, Akbar the Great. His father was Jahangir, another well-known Mughal ruler, and his mother was Jagat Gosain, a Rajput princess. So yeah, royal blood flowed generously through his veins.
From an early age, Khurram showed signs of being an able prince. He was intelligent, brave, and ambitious. Akbar had a soft corner for him, and Jahangir, though often busy with court politics, recognized his son’s potential.
The Rise to Power

Let’s not sugarcoat it—Mughal succession wasn’t a peaceful affair. Shah Jahan didn’t just inherit the throne with a smile and a crown. Nope. Like most Mughal emperors, he had to fight for it.
After Jahangir’s death in 1627, the Mughal throne was up for grabs. Prince Khurram, who already had military victories under his belt, declared himself the rightful heir. But, surprise surprise, not everyone agreed. A bit of civil war broke out between him and his brothers (and other claimants), but he eventually emerged victorious and became emperor in 1628.
That’s when he took the regal name Shah Jahan, which means “King of the World.” Modest? Not quite. But definitely iconic.
An Emperor with Style
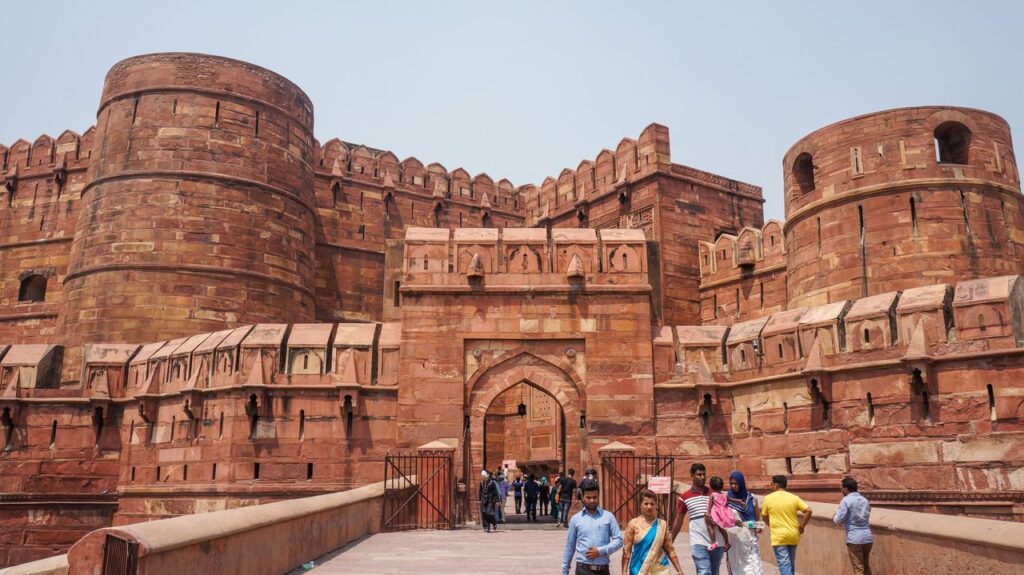

Shah Jahan’s reign is often called the Golden Age of Mughal architecture, and for good reason. The man had taste—expensive, grand, and elegant taste.
He built the Red Fort in Delhi, the Jama Masjid, sections of the Agra Fort, and of course, the glorious Taj Mahal. Under his rule, the Mughal court was the epitome of luxury. Think silk robes, intricate jewelry, delicately painted miniatures, and gardens that looked like paradise on Earth.
And the empire? It was massive—stretching from the Deccan in the south to Kabul in the north. It was wealthy, powerful, and culturally vibrant. Shah Jahan made sure it looked the part.
The Love Story That Touched the Sky

Now let’s talk about the part of Shah Jahan’s story that tugs at everyone’s heartstrings—his love for Mumtaz Mahal.
Mumtaz, whose real name was Arjumand Banu Begum, was his second wife but undoubtedly his favorite. The two were inseparable. She wasn’t just a pretty face—she was his advisor, companion, and the love of his life. She even accompanied him on military campaigns!
Tragically, in 1631, while giving birth to their 14th child (yes, 14th!), Mumtaz died. Shah Jahan was devastated. Legend says he locked himself away in grief, and when he reappeared, his hair had turned gray.
Out of his sorrow, he decided to build a monument unlike any other—the Taj Mahal. It took over 20 years and thousands of workers to complete. But when it was done, it stood as a testament to eternal love—a tomb that looked like a dream in white marble.
Seriously, who else builds a palace just to say “I miss you”?
The Not-So-Happy Ending
As grand as his rule was, Shah Jahan’s life didn’t end with a royal farewell. In a tragic twist, he was overthrown by his own son, Aurangzeb, in 1658.
Aurangzeb, who was a strict and ambitious ruler, saw his father’s declining health and seized the throne. Shah Jahan was placed under house arrest in Agra Fort, where he spent the last eight years of his life.
Here’s the poetic part—his room had a window that gave him a direct view of the Taj Mahal. So he spent his days gazing at the monument he built for his beloved Mumtaz. Some say he died with his eyes fixed on it.
In 1666, Shah Jahan passed away and was buried next to Mumtaz Mahal in the Taj, forever reunited with her in the house of love he built.
His Legacy
Even though Shah Jahan’s end was bittersweet, his legacy is nothing short of legendary.
He gave India some of its most iconic architectural masterpieces. The Taj Mahal alone attracts millions of visitors every year and is considered one of the Seven Wonders of the World.
But beyond the buildings, Shah Jahan represented the zenith of Mughal cultural achievement. Art, literature, music, and architecture flourished during his rule. His court was a melting pot of Persian, Indian, and Islamic influences, creating a unique and beautiful Mughal identity.
He wasn’t perfect—he could be ruthless when it came to politics, and his lavish lifestyle may have drained the treasury—but as a ruler, he balanced power with vision.
Some Lesser-Known Fun Facts
- Shah Jahan was a patron of science and had a keen interest in astronomy.
- His court was home to several scholars and poets, including the famous historian Abdul Hamid Lahori.
- Though he had multiple wives, his love for Mumtaz was legendary—even their court poets couldn’t stop writing about it.
- He once planned to build a Black Taj Mahal opposite the white one across the Yamuna River, but the plan was abandoned after his imprisonment.
Wrapping It Up
Shah Jahan’s life had all the makings of an epic movie—royalty, romance, war, betrayal, and legacy. He was a king who loved deeply, dreamed grandly, and ruled magnificently.
Even centuries later, his story continues to move people, especially those who’ve stood before the Taj Mahal and felt the love and loss etched into every marble stone.
So the next time you see a picture of the Taj, remember—behind that majestic dome is a tale of a man who turned grief into glory, and who gave the world a monument that whispers, “Love lives on.”






































































































0 Comments