Here are facts about Raja Ram Mohan Roy, one of the most influential social reformers in Indian history:
Raja Ram Mohan Roy was a visionary, social reformer, and intellectual giant who played a pivotal role in shaping modern India. Known as the “Father of the Indian Renaissance” and the “Father of Modern India,” his efforts in reforming society, advocating for education, and challenging orthodox traditions laid the foundation for a progressive and enlightened nation. Through his fearless activism, he brought attention to the need for social change and rational thinking in 19th-century India.
Early Life and Education

Raja Ram Mohan Roy was born on May 22, 1772, in Radhanagar, a small village in Bengal Presidency, now in West Bengal, India. He was born into a well-to-do Brahmin family. His father, Ramkanta Roy, was a conservative Hindu, while his mother, Tarini Devi, was deeply religious.
From a young age, Ram Mohan Roy showed an eagerness to learn. He studied multiple languages including Sanskrit, Persian, Arabic, and later English. His exposure to different religious texts such as the Vedas, Upanishads, the Quran, and the Bible helped him develop a critical and comparative understanding of religions. This multilingual and multicultural education would later shape his reformist ideology.
A Visionary Social Reformer

Ram Mohan Roy was deeply disturbed by the social evils and orthodox practices prevailing in Indian society during his time. He believed in the rational interpretation of scriptures and sought to purify Hinduism by removing superstitions and harmful customs.
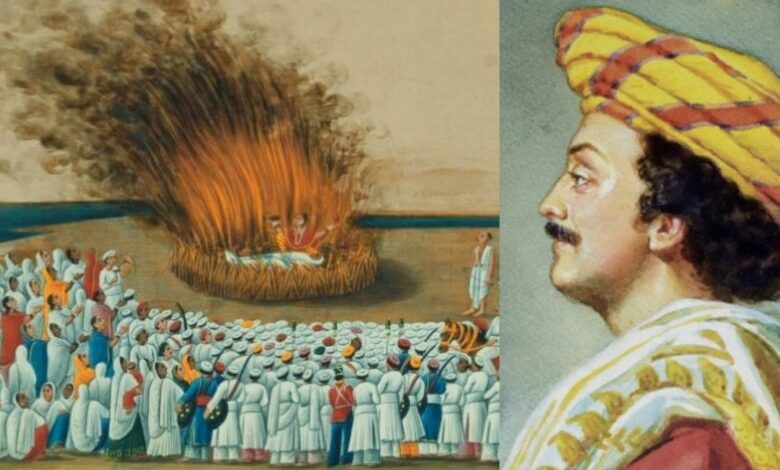
Abolition of Sati
One of his most significant contributions was his campaign against the practice of Sati—the custom where widows were burned alive on the funeral pyres of their husbands. Ram Mohan Roy was horrified by this inhumane ritual and actively worked for its abolition. He wrote essays, petitioned the British authorities, and raised public awareness.
His relentless efforts led to the abolition of Sati in 1829 by Lord William Bentinck, the Governor-General of India. This was a landmark moment in Indian history and marked the beginning of organized social reform movements.
Opposition to Caste Discrimination and Idolatry
Roy also opposed the rigid caste system and the practice of untouchability, which divided society and oppressed marginalized communities. He believed that such discrimination had no place in a civilized society.
He was also against idol worship, which he viewed as a distortion of the true spiritual message of Hinduism. Instead, he promoted the idea of a formless, monotheistic God, drawing inspiration from the Upanishads and Vedantic texts.
The Brahmo Samaj: A Religious and Social Revolution

In 1828, Ram Mohan Roy founded the Brahmo Samaj, a reformist religious movement that aimed to promote monotheism, social equality, and ethical living. The Brahmo Samaj became a platform for addressing various issues such as:
- Women’s rights
- Education reform
- Religious tolerance
- Opposition to superstitions and rituals
The movement welcomed people from all castes and religions and played a major role in the Indian Renaissance. It paved the way for later reformers like Ishwar Chandra Vidyasagar, Keshab Chandra Sen, and Swami Vivekananda.
Pioneer of Modern Education

Ram Mohan Roy recognized the power of education as a tool for social transformation. He advocated for Western education, especially in subjects like science, mathematics, and philosophy, to help Indians compete in a changing world.
He established Anglo-Hindu schools that blended traditional Indian learning with modern subjects. In 1822, he founded the Anglo-Hindu School in Kolkata and later helped establish the Hindu College (now Presidency University).
He also supported women’s education at a time when educating girls was considered taboo. He believed that educated women would not only uplift themselves but also play a critical role in the progress of society.
Promotion of Freedom of Press and Civil Rights

Raja Ram Mohan Roy was a champion of free speech and freedom of the press. He launched several newspapers and journals to spread awareness and promote rational thinking. These included:
- Sambad Kaumudi (Bengali)
- Mirat-ul-Akbar (Persian)
- Brahmanical Magazine (English)
Through these publications, he discussed important social, political, and religious issues. He encouraged Indians to think independently, question authority, and stand up against injustice.
He also appealed to the British authorities for the rights of Indian citizens, including equality before the law, administrative reforms, and the protection of civil liberties.
Work in the West and Death
In 1830, Raja Ram Mohan Roy traveled to England as an ambassador of the Mughal Emperor Akbar II, who had bestowed upon him the title Raja. His mission was to plead for the Emperor’s pension and also to advocate for Indian interests.
During his time in Britain, he met many political leaders, intellectuals, and reformers. He explained the richness of Indian culture and argued for India’s right to dignity and self-governance.
Sadly, he died in Bristol, England, on September 27, 1833, at the age of 61. He was buried there, and his tomb remains a site of reverence for admirers from India and around the world.
Legacy and Influence
Raja Ram Mohan Roy’s legacy is monumental. He was a pioneer of modern Indian thought, and his contributions continue to shape the country’s social and cultural fabric.
Key Contributions:
- Abolished Sati and promoted women’s rights
- Founded the Brahmo Samaj
- Promoted education and rationalism
- Laid the foundation for modern journalism in India
- Advocated for social justice and civil liberties
He inspired generations of social reformers and nationalists, including Mahatma Gandhi, Rabindranath Tagore, and Jawaharlal Nehru.
In recognition of his contributions, the Indian government observes May 22 as Raja Ram Mohan Roy Jayanti, celebrating his role in shaping a modern, progressive India.





































































































0 Comments