Here are 80 fascinating facts about the Royal Bengal Tiger (Panthera tigris tigris) — India’s national animal and one of the most iconic big cats in the world:
Imagine a creature that’s both majestic and deadly, powerful and graceful, beautiful and fearsome. That’s the Royal Bengal Tiger for you—a living symbol of India’s wildlife and one of the most iconic big cats on the planet. With its piercing amber eyes, thick orange coat with black stripes, and that stealthy, confident walk, the Bengal tiger doesn’t just own the jungle—it rules it.
Whether you’ve seen it in documentaries, read about it in school, or heard about it from wildlife lovers, there’s something almost mythical about this magnificent beast. So, let’s take a fun, informal dive into the life and world of the Royal Bengal Tiger—its history, its lifestyle, and why it deserves every bit of the awe and attention it gets.
Meet the Royal Bengal Tiger
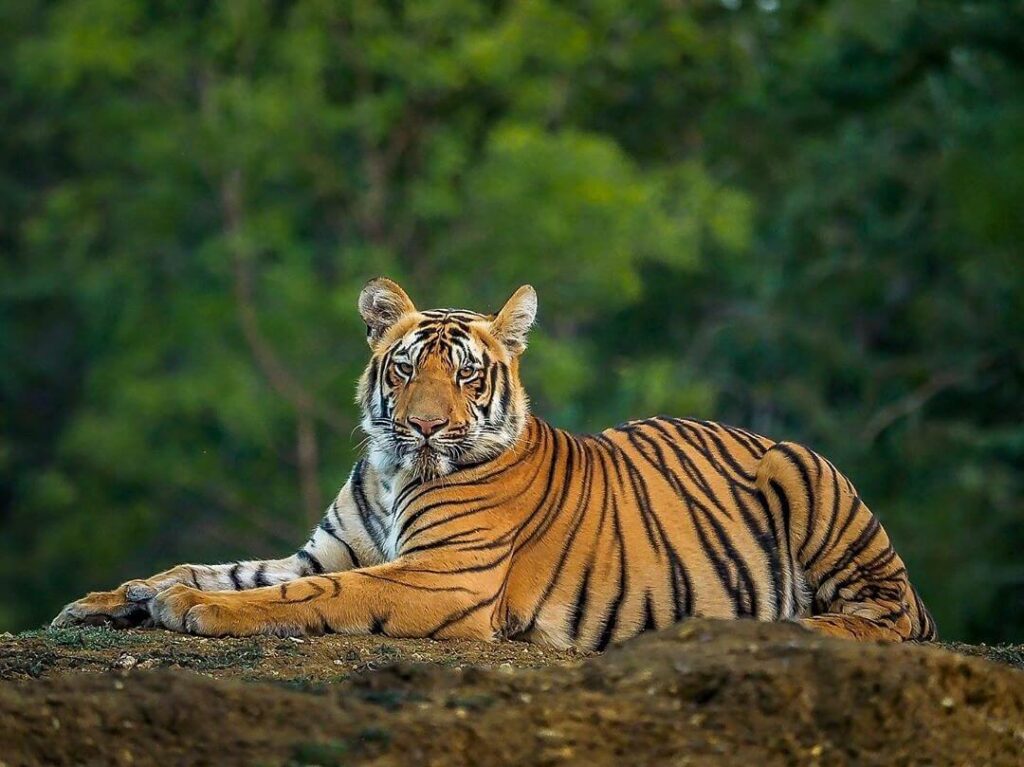

The Royal Bengal Tiger, scientifically known as Panthera tigris tigris, is a subspecies of the tiger and is primarily found in India, though smaller populations exist in Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, and Myanmar. It is India’s national animal, and for good reason—it represents strength, courage, and the untamed spirit of the wild.
Adult male Bengal tigers can weigh up to 220–250 kilograms (485–550 lbs) and grow up to 3 meters (10 feet) in length including their tail. Females are usually a bit smaller, but just as fierce. These are massive animals, but they move with a grace that’s almost hypnotic.
What’s unique about them? Well, every tiger’s stripe pattern is like a fingerprint—no two are the same. These stripes aren’t just for show either; they help the tiger blend into the tall grass and forest shadows while stalking prey. Camouflage, but make it fashion.
Where They Live: From Forests to Mangroves
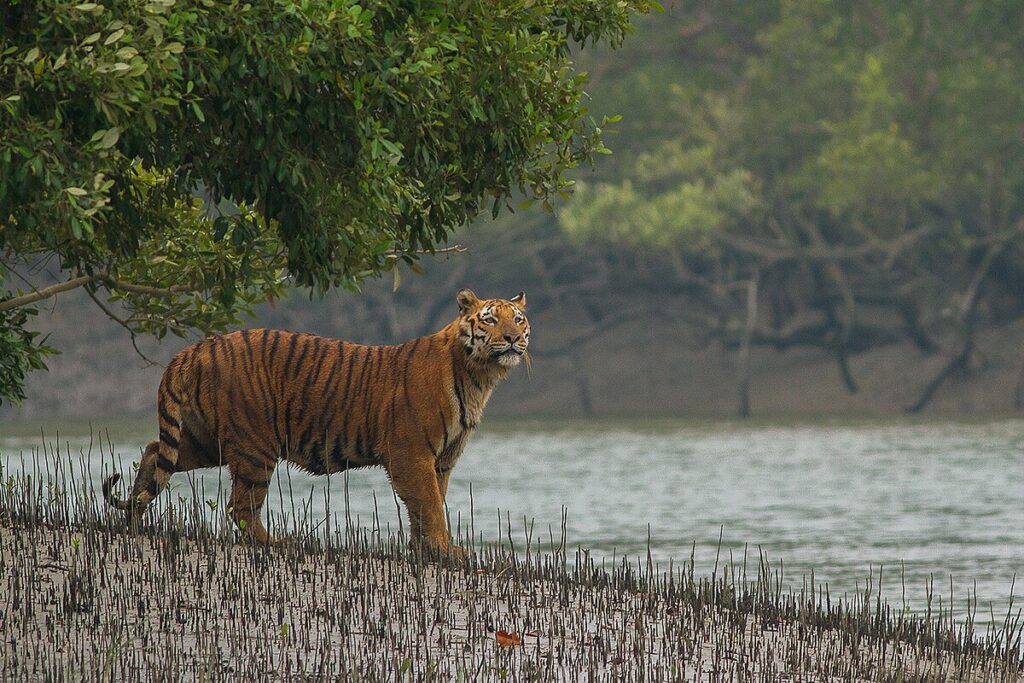

Royal Bengal tigers are adaptable animals. They live in a wide range of habitats—dense forests, grasslands, mangroves, and even wetlands. Some of the most famous tiger habitats in India include:
- Sundarbans (West Bengal): A mangrove forest where land and water mix, making it a perfect (and pretty dangerous) home for tigers.
- Ranthambhore (Rajasthan): A dry, rugged forest with ancient ruins—basically a jungle movie set.
- Bandhavgarh and Kanha (Madhya Pradesh): Lush forests full of prey, perfect for tiger spotting.
- Jim Corbett (Uttarakhand): India’s oldest national park and a great place to try your luck at seeing one in the wild.
What’s fascinating is how Bengal tigers adapt their behavior depending on their environment. In the Sundarbans, for example, tigers are known to swim for miles and have learned to live with tidal changes. Yes, these guys can swim really well, which is honestly kind of terrifying and cool at the same time.
A Day in the Life of a Bengal Tiger

If you think tigers are constantly on the move or hunting 24/7, think again. These big cats are actually pretty chill most of the day. They’re mostly nocturnal, which means they hunt at night and sleep during the day—about 16 to 20 hours of napping daily. Living the dream, right?
When they do decide it’s hunting time, they rely on their stealth and powerful muscles to ambush prey. Their diet mainly includes deer, wild boars, and sometimes even buffalo. They prefer to hunt alone and go in for the kill with a quick bite to the neck or back of the head. Brutal, efficient, and silent—it’s no wonder they’re apex predators.
Tigers are also highly territorial. A single tiger may claim a territory of 20 to 100 square kilometers, depending on the environment and availability of prey. They use scent markings, scratch marks on trees, and roars to tell others to stay off their turf.
Baby Tigers: Cuteness Overload
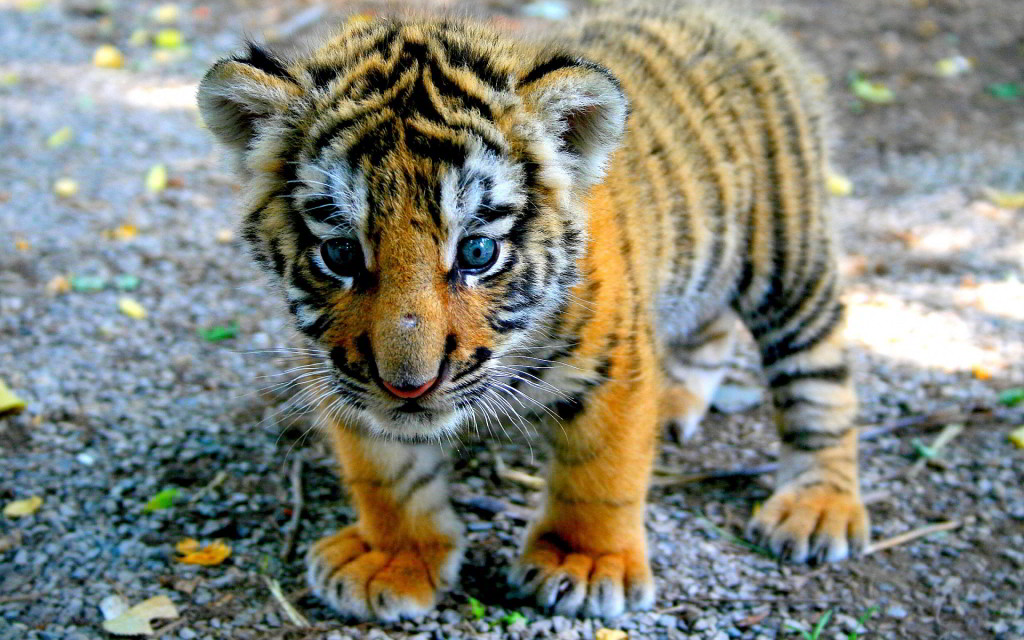

Tiger cubs? Oh yes, they are adorable. When a tigress gives birth, she usually has 2 to 4 cubs at a time. These little fluff balls are born blind and totally dependent on their mom for the first few weeks.
The mother is super protective—she raises them all by herself and teaches them everything from hunting to surviving on their own. Cubs stay with their mom for about two years, after which they venture out to find their own territories.
Sadly, cub mortality is high. Only about half of the tiger cubs survive past the age of two, due to predation, accidents, or even fights with other tigers.
Why Are They Endangered?

This is the part of the story that gets a little dark. Despite their size and strength, Bengal tigers are endangered. Why? Well, here are the main reasons:
- Habitat loss: As forests are cut down for agriculture, roads, and development, tigers lose their homes.
- Poaching: Tigers are hunted illegally for their skin, bones, and other body parts, which are used in traditional medicine and sold on the black market.
- Human-wildlife conflict: When tigers roam into villages or farmlands, they’re often killed out of fear or to protect livestock.
There were once estimated to be over 100,000 tigers in the wild just a century ago. Today, that number has dropped dramatically. As of the latest counts, India has around 3,000 wild Bengal tigers, which actually makes it the country with the largest tiger population in the world—but it’s still a fragile number.
The Fight to Save the Tigers
Thankfully, there’s hope. India launched Project Tiger back in 1973, and it’s been one of the world’s most successful conservation efforts. National parks and tiger reserves were created, anti-poaching laws were strengthened, and awareness campaigns kicked off.
Today, tiger conservation is a big deal—not just among wildlife experts but also among ordinary people, photographers, and influencers. The recent tiger census even involved camera traps, GPS collars, and drones to track the animals more safely and accurately.
Tigers are also important to the ecosystem. As apex predators, they keep prey populations in check, which in turn helps maintain the balance of vegetation and the health of the forest.
Tigers in Culture and Pop Culture
Tigers have long been a part of Indian mythology, art, and folklore. Remember Goddess Durga riding a tiger as she slays demons? That’s not just badass—it’s symbolic of power, protection, and divine strength.
In pop culture, Bengal tigers have had their share of stardom too. Think of:
- Richard Parker from Life of Pi (a Bengal tiger that pretty much stole the show).
- The tiger in Rudyard Kipling’s The Jungle Book (though Shere Khan was more villain than hero).
- Countless documentaries and wildlife shows that showcase tigers stalking through grasslands in slow motion.
Tigers are a symbol of wild beauty, and they never fail to stir up emotion—whether it’s awe, respect, or a bit of fear.
Final Roar: Why We Need to Care
So, what can we take away from all this? The Royal Bengal Tiger isn’t just a big cat lounging in the jungle. It’s a symbol of wild India, a vital part of our ecosystem, and a species that deserves our respect and protection.
If we lose the tiger, we lose more than just a majestic animal—we risk upsetting the natural balance of entire forests and ecosystems. Saving tigers isn’t just about loving wildlife—it’s about preserving nature for future generations.
So, the next time you see a photo of a tiger or hear a story about one, take a moment to appreciate the awe-inspiring creature that it is. And maybe—just maybe—you’ll feel inspired to support tiger conservation in your own way.
Because the jungle just wouldn’t be the same without its royal king. 🐅👑





































































































0 Comments