Here are 100 facts about Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj, one of the most respected and influential figures in Indian history:
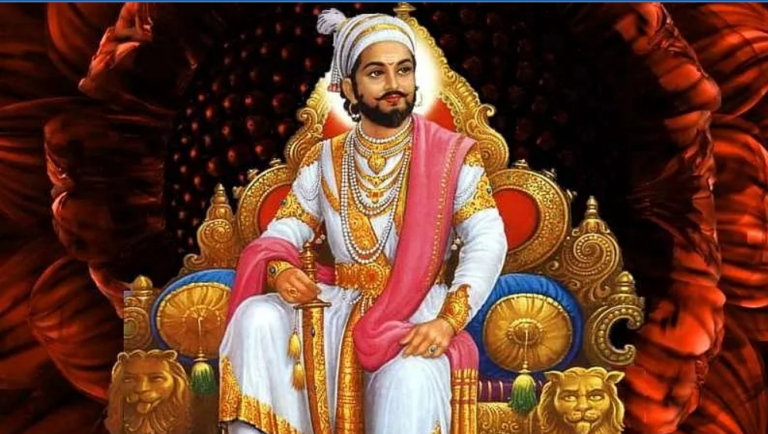
- Chhatrapati Shivaji Maharaj was born on February 19, 1630, at Shivneri Fort near Pune, Maharashtra.
- He was the son of Shahaji Bhosale and Jijabai.
- His father’s name was Shahaji Raje Bhosale, a Maratha general who served in the Deccan Sultanates.
- His mother, Jijabai, was an inspiration for his life, teaching him about bravery, righteousness, and the importance of Hindu culture.
- Shivaji was crowned as the Chhatrapati (Emperor) of the Maratha Empire on June 6, 1674, at Raigad Fort.
- He founded the Maratha Empire and expanded its power over a large part of western India.
- His iconic grand coronation at Raigad is considered one of the most important events in Indian history.
- He established a strong navy to protect the western coastline of India and trade routes.
- Shivaji Maharaj’s motto was “Hindavi Swarajya”, meaning “Swarajya (self-rule) for Hindus.”
- He is known for his innovative military tactics and guerrilla warfare strategies.
- His guerrilla warfare tactics included rapid attacks, ambushes, and swift retreats, making it difficult for the larger Mughal armies to defeat him.
- Shivaji Maharaj was crowned by Gagabhat (a Hindu priest) in a traditional Maratha ceremony at Raigad Fort.
- He created a strong administrative system with a council of ministers and a well-organized bureaucracy.
- He established a network of forts, including Raigad, Sindhudurg, and Pratapgad, among others.
- He ensured that the Maratha state was built on principles of social justice, religious tolerance, and cultural pride.
- Shivaji Maharaj took the title “Chhatrapati”, meaning “Lord of the umbrella,” symbolizing his leadership and authority.
- He had a total of eight wives and many sons, but his primary consort was Saibai Nimbalkar.
- His mother, Jijabai, played a pivotal role in shaping his character and ideals.
- Shivaji’s early military career began with the capture of the Torna Fort at the age of 16.
- He founded the Hindu Pad Padshahi (the kingdom of Hindu kingship) to secure the rule of Hindus over India.
- Shivaji Maharaj had a fortress strategy that made the Maratha Empire very difficult to defeat by conventional forces.
- His navy helped in defending the western coastline from foreign invaders, particularly the Portuguese and the English.
- He started the Shivaji’s military reforms, focusing on the well-being of his soldiers and making them self-sufficient.
- Shivaji had a flawless system of intelligence—he was known for spying on his enemies and using information to his advantage.
- His forts in the Sahyadri mountain range were strategically built and played a key role in Maratha defense.
- His rise to power was marked by a conflict with Bijapur Sultanate when he seized several forts under their control.
- Shivaji Maharaj was an expert in naval warfare, building a fleet to protect the Konkan coast.
- The fort of Sindhudurg, built by Shivaji Maharaj, is still considered one of the most formidable marine forts in India.
- Shivaji Maharaj’s intelligence network was extensive, with spies placed in all strategic locations.
- He established the Maval region as a key base for his military operations.
- Shivaji’s reign was characterized by the establishment of a just and fair tax system.
- Shivaji Maharaj was deeply committed to religious freedom and upheld the principles of tolerance and respect for all religions.
- He used his navy to counter pirates and foreign invaders, particularly the Portuguese and the British.
- Shivaji Maharaj had a strong sense of administrative leadership and was known for being a compassionate and wise ruler.
- Raigad Fort served as the capital of Shivaji’s kingdom.
- He ensured the welfare of the peasants and the overall growth of agriculture in his kingdom.
- Shivaji Maharaj established the concept of a welfare state, where the king was considered the protector of his subjects.
- He made the Swarajya (self-rule) and Bharatiya (Indian) pride central themes of his governance.
- He encouraged trade and commerce, strengthening the economy of his empire.
- Shivaji Maharaj was known for his justice and fairness, often listening to his subjects’ grievances directly.
- He established a strong military system with separate departments for artillery, cavalry, and infantry.
- He was fiercely loyal to his people, making his army a close-knit, disciplined unit.
- The Maratha Empire expanded under Shivaji Maharaj’s leadership, incorporating territories from southern Maharashtra to northern Karnataka.
- Shivaji Maharaj took the oath to free the land of Hindus from foreign rule.
- He had a strong sense of national identity and sought to protect India from foreign invasions.
- He used diplomacy effectively to gain alliances with other regional powers against common enemies.
- Shivaji Maharaj captured the Kondana Fort (now known as Sinhagad Fort) from Bijapur forces.
- He fought and defeated Afzal Khan, a powerful general of the Bijapur Sultanate, in the famous Battle of Pratapgad.
- Afzal Khan’s death during the battle helped cement Shivaji’s rise as a regional leader.
- Shivaji Maharaj was the first Maratha king to receive the title of Chhatrapati, signifying the highest authority.
- He was a patron of culture, encouraging arts, music, and literature in his kingdom.
- He had a deep respect for Indian classical arts and promoted local artists.
- Shivaji Maharaj maintained diplomatic relations with the Mughal Empire, but he also fiercely resisted their attempts at domination.
- He set up a network of fortresses along the western coast to defend against naval invasions.
- Shivaji Maharaj’s tactics at sea were vital in protecting his coastal kingdom from Portuguese and Dutch forces.
- The Mavla troops, known for their courage and bravery, played a critical role in his military conquests.
- Shivaji Maharaj abolished the traditional feudal taxes and implemented more fair and equitable tax policies.
- He was a skilled administrator, creating a balanced and just governance system.
- Shivaji Maharaj had a deep respect for his warriors, giving them land and wealth in return for their loyalty and bravery.
- He instituted the Hindavi Swarajya (self-rule for Hindus) as the goal of his empire.
- He was a visionary leader, bringing together a diverse set of people and cultures under his rule.
- He had a strong sense of egalitarianism, promoting equal opportunities for all sections of society.
- Shivaji Maharaj is often depicted riding a horse named ‘Chetak’ and was known for his bravery in battle.
- He was a skilled diplomat, outsmarting larger empires, including the Mughal Empire.
- Shivaji’s kingdom, under his leadership, became a beacon of hope for Hindus during a time of Muslim domination.
- Shivaji Maharaj’s military was one of the first in India to employ well-trained and disciplined soldiers.
- He was known for his kindness and fairness toward the common people and often took personal interest in their welfare.
- Shivaji Maharaj was deeply devoted to Lord Shiva and used the symbol of a lion (Shivaji’s signature emblem) as his symbol.
- He successfully defended his territories against both the Mughal Empire and the Deccan Sultanates.
- He set up a network of forts along the Konkan coast to strengthen maritime defenses.
- Shivaji Maharaj established a navy that was a major force in the Indian Ocean, protecting the coast from foreign invaders.
- He was highly respected by his allies for his integrity, leadership, and fearlessness.
- Shivaji’s army had no religious discrimination, and people from different backgrounds and faiths served under him.
- The Shivaji Maharaj Museum in Pune is dedicated to his legacy.
- He introduced the concept of guerrilla warfare in India and is celebrated for his innovative battle tactics.
- Shivaji Maharaj was an admirer of Indian classical music and arts.
- He took significant steps to restore Hindu temples that had been destroyed by foreign invaders.
- He is considered one of the greatest military tacticians of his time.
- Shivaji Maharaj’s family played a critical role in his campaigns, with many of his relatives serving in key military positions.
- He led the Maratha forces to victory in several battles, including the Battle of Surat.
- Shivaji Maharaj is considered a symbol of resistance against tyranny and foreign domination.
- He was known for his steadfastness in holding his ground during difficult times.
- Shivaji’s reign marked the beginning of the Maratha Empire, which later expanded to become a significant power in India.
- He is celebrated as a hero not only in Maharashtra but throughout India for his contribution to the country’s defense and unity.
- He was a patron of agriculture, introducing several reforms to improve the livelihoods of farmers.
- Shivaji Maharaj’s death in 1680 was a major blow to the Maratha Empire, but his legacy endured through his successors.
- His leadership inspired other rulers to take up arms against foreign invaders and regional despots.
- Shivaji Maharaj created a legal code that ensured justice, safety, and equity for his subjects.
- His military prowess was admired even by his enemies, including the Mughals and the Sultanates of the Deccan.
- He was the first ruler to recognize the importance of a naval defense for coastal territories.
- His soldiers were highly disciplined, and he gave them not only land but also security and respect.
- Shivaji Maharaj was a true patriot, fighting for the freedom and welfare of his people.
- He was also known for his benevolence toward common citizens, granting them protection against cruelty and oppression.
- His empire had a highly effective system of taxation, ensuring a steady source of revenue.
- He built several mighty forts, such as Rajgad and Torna, which played crucial roles in his military strategies.
- Shivaji Maharaj’s legacy as a warrior and a ruler has been preserved in numerous books, films, and documentaries.
- His empire had a strong economy, driven by agriculture, trade, and innovative administrative reforms.
- Shivaji Maharaj’s rule was characterized by religious tolerance, where Hindus, Muslims, and other communities lived peacefully.
- Shivaji Maharaj’s concept of Swarajya (self-rule) was ahead of his time, inspiring future generations to seek political autonomy.
- Shivaji Maharaj’s name continues to evoke patriotism and pride in India, making him an enduring symbol of valor, justice, and patriotism.





















0 Comments